by Aleena Parvez | Nov 6, 2025
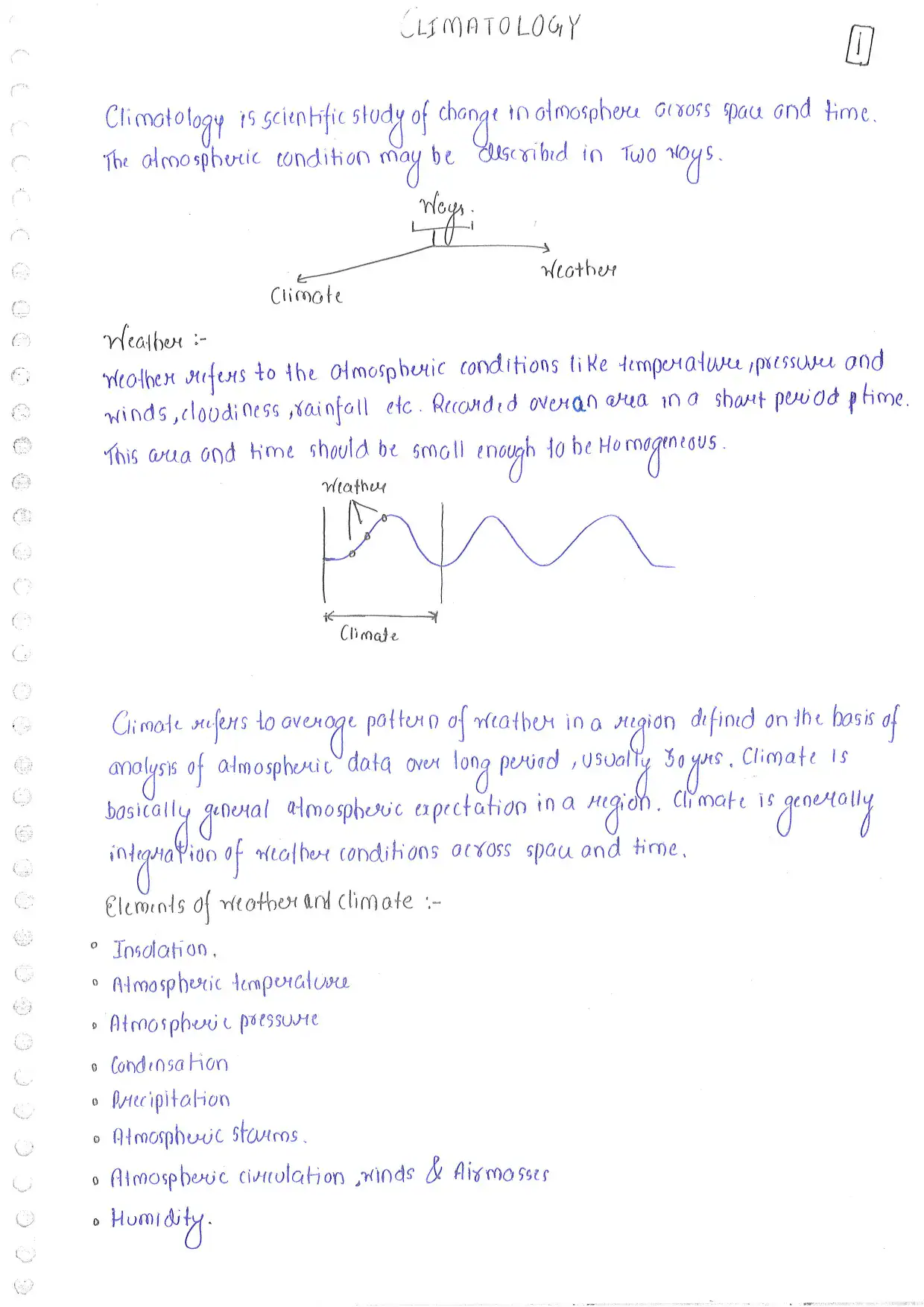
This file is a comprehensive set of notes on Climatology, covering the fundamental concepts of atmospheric changes, weather versus climate, elements of weather and climate, atmospheric structure, temperature distribution (horizontal and vertical), atmospheric pressure, condensation and precipitation mechanisms, types of winds, airmasses, weather fronts, jet streams, and global climatic classifications (such as Koppen’s system). It provides detailed explanations of climate processes, causes of climatic phenomena, and global patterns relevant for undergraduate geography study.
by Yash Sharma | Nov 3, 2025
Time series: observations of well-defined data at regular intervals (weekly/monthly/yearly). Components: trend (long-term), cyclical (1-7 years), seasonal (yearly), irregular (random). Models: multiplicative (Y=T×C×S×I), additive (Y=T+C+S+I). Moving average smoothing for forecasting.
by Yash Sharma | Nov 3, 2025
Sampling methods: probability (simple random, stratified, cluster, multistage) vs non-probability (purposive, convenience). Simple random: equal independent chance, requires population list. Stratified: heterogeneous subpopulations. Cluster: cost-effective. Multistage: widely spread populations.
by Yash Sharma | Nov 3, 2025
Forecasting: reliable estimates of uncertain future events using historical data. Types: demand, environmental, technological. Timing: short-range (<3 months), medium-range (3-12 months), long-range (3+ years). Methods: qualitative (personal opinion, Delphi), quantitative (freehand, smoothing, trend).
by Yash Sharma | Nov 3, 2025
Dunlop system approach: participants (workers, management, government), environmental forces (technology, market, power). Craig framework: inputs, processes, outputs, feedback loops. System components interact within boundaries. Output: network of rules, labor policy, agreements ensuring fair worker treatment.
